19 KiB
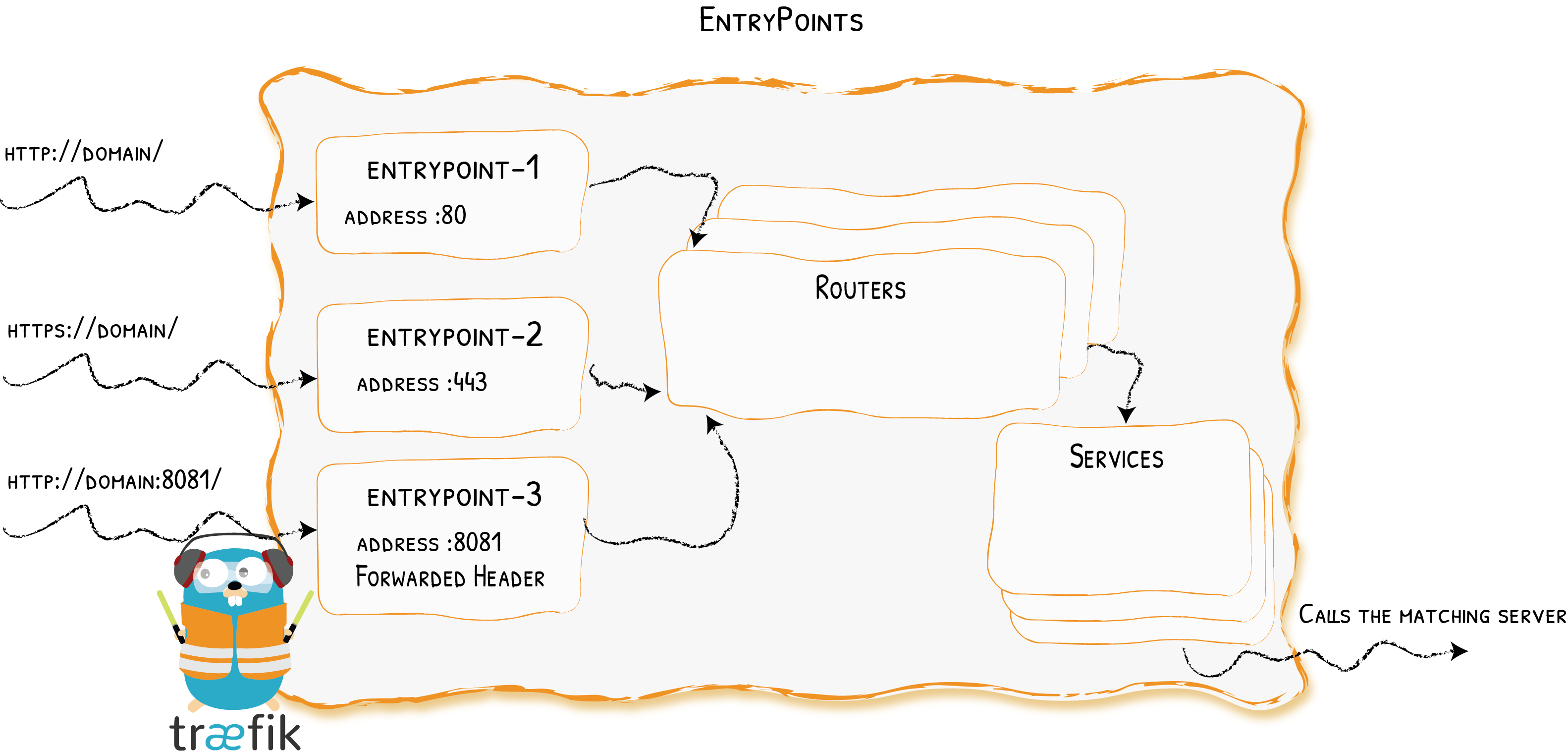
EntryPoints
Opening Connections for Incoming Requests {: .subtitle }
EntryPoints are the network entry points into Traefik. They define the port which will receive the packets, and whether to listen for TCP or UDP.
Configuration Examples
??? example "Port 80 only"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
```
We define an `entrypoint` called `web` that will listen on port `80`.
??? example "Port 80 & 443"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.websecure]
address = ":443"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
websecure:
address: ":443"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
--entryPoints.websecure.address=:443
```
- Two entrypoints are defined: one called `web`, and the other called `websecure`.
- `web` listens on port `80`, and `websecure` on port `443`.
??? example "UDP on port 1704"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.streaming]
address = ":1704/udp"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
streaming:
address: ":1704/udp"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.streaming.address=:1704/udp
```
Configuration
General
EntryPoints are part of the static configuration. You can define them using a toml file, CLI arguments, or a key-value store.
??? info "See the complete reference for the list of available options"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.name]
address = ":8888" # same as ":8888/tcp"
[entryPoints.name.transport]
[entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle]
requestAcceptGraceTimeout = 42
graceTimeOut = 42
[entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts]
readTimeout = 42
writeTimeout = 42
idleTimeout = 42
[entryPoints.name.proxyProtocol]
insecure = true
trustedIPs = ["127.0.0.1", "192.168.0.1"]
[entryPoints.name.forwardedHeaders]
insecure = true
trustedIPs = ["127.0.0.1", "192.168.0.1"]
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
name:
address: ":8888" # same as ":8888/tcp"
transport:
lifeCycle:
requestAcceptGraceTimeout: 42
graceTimeOut: 42
respondingTimeouts:
readTimeout: 42
writeTimeout: 42
idleTimeout: 42
proxyProtocol:
insecure: true
trustedIPs:
- "127.0.0.1"
- "192.168.0.1"
forwardedHeaders:
insecure: true
trustedIPs:
- "127.0.0.1"
- "192.168.0.1"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.name.address=:8888 # same as :8888/tcp
--entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle.requestAcceptGraceTimeout=42
--entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle.graceTimeOut=42
--entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts.readTimeout=42
--entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts.writeTimeout=42
--entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts.idleTimeout=42
--entryPoints.name.proxyProtocol.insecure=true
--entryPoints.name.proxyProtocol.trustedIPs=127.0.0.1,192.168.0.1
--entryPoints.name.forwardedHeaders.insecure=true
--entryPoints.name.forwardedHeaders.trustedIPs=127.0.0.1,192.168.0.1
```
Address
The address defines the port, and optionally the hostname, on which to listen for incoming connections and packets. It also defines the protocol to use (TCP or UDP). If no protocol is specified, the default is TCP. The format is:
[host]:port[/tcp|/udp]
If both TCP and UDP are wanted for the same port, two entryPoints definitions are needed, such as in the example below.
??? example "Both TCP and UDP on port 3179"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.tcpep]
address = ":3179"
[entryPoints.udpep]
address = ":3179/udp"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
tcpep:
address: ":3179"
udpep:
address: ":3179/udp"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.tcpep.address=:3179
--entryPoints.udpep.address=:3179/udp
```
Forwarded Headers
You can configure Traefik to trust the forwarded headers information (X-Forwarded-*).
??? info "forwardedHeaders.trustedIPs"
Trusting Forwarded Headers from specific IPs.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.web.forwardedHeaders]
trustedIPs = ["127.0.0.1/32", "192.168.1.7"]
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
forwardedHeaders:
trustedIPs:
- "127.0.0.1/32"
- "192.168.1.7"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
--entryPoints.web.forwardedHeaders.trustedIPs=127.0.0.1/32,192.168.1.7
```
??? info "forwardedHeaders.insecure"
Insecure Mode (Always Trusting Forwarded Headers).
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.web.forwardedHeaders]
insecure = true
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
forwardedHeaders:
insecure: true
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
--entryPoints.web.forwardedHeaders.insecure
```
Transport
respondingTimeouts
respondingTimeouts are timeouts for incoming requests to the Traefik instance.
Setting them has no effect for UDP entryPoints.
??? info "transport.respondingTimeouts.readTimeout"
_Optional, Default=0s_
`readTimeout` is the maximum duration for reading the entire request, including the body.
If zero, no timeout exists.
Can be provided in a format supported by [time.ParseDuration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration) or as raw values (digits).
If no units are provided, the value is parsed assuming seconds.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.name]
address = ":8888"
[entryPoints.name.transport]
[entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts]
readTimeout = 42
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
name:
address: ":8888"
transport:
respondingTimeouts:
readTimeout: 42
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.name.address=:8888
--entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts.readTimeout=42
```
??? info "transport.respondingTimeouts.writeTimeout"
_Optional, Default=0s_
`writeTimeout` is the maximum duration before timing out writes of the response.
It covers the time from the end of the request header read to the end of the response write.
If zero, no timeout exists.
Can be provided in a format supported by [time.ParseDuration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration) or as raw values (digits).
If no units are provided, the value is parsed assuming seconds.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.name]
address = ":8888"
[entryPoints.name.transport]
[entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts]
writeTimeout = 42
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
name:
address: ":8888"
transport:
respondingTimeouts:
writeTimeout: 42
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.name.address=:8888
--entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts.writeTimeout=42
```
??? info "transport.respondingTimeouts.idleTimeout"
_Optional, Default=180s_
`idleTimeout` is the maximum duration an idle (keep-alive) connection will remain idle before closing itself.
If zero, no timeout exists.
Can be provided in a format supported by [time.ParseDuration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration) or as raw values (digits).
If no units are provided, the value is parsed assuming seconds.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.name]
address = ":8888"
[entryPoints.name.transport]
[entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts]
idleTimeout = 42
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
name:
address: ":8888"
transport:
respondingTimeouts:
idleTimeout: 42
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.name.address=:8888
--entryPoints.name.transport.respondingTimeouts.idleTimeout=42
```
lifeCycle
Controls the behavior of Traefik during the shutdown phase.
??? info "lifeCycle.requestAcceptGraceTimeout"
_Optional, Default=0s_
Duration to keep accepting requests prior to initiating the graceful termination period (as defined by the `graceTimeOut` option).
This option is meant to give downstream load-balancers sufficient time to take Traefik out of rotation.
Can be provided in a format supported by [time.ParseDuration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration) or as raw values (digits).
If no units are provided, the value is parsed assuming seconds.
The zero duration disables the request accepting grace period, i.e., Traefik will immediately proceed to the grace period.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.name]
address = ":8888"
[entryPoints.name.transport]
[entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle]
requestAcceptGraceTimeout = 42
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
name:
address: ":8888"
transport:
lifeCycle:
requestAcceptGraceTimeout: 42
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.name.address=:8888
--entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle.requestAcceptGraceTimeout=42
```
??? info "lifeCycle.graceTimeOut"
_Optional, Default=10s_
Duration to give active requests a chance to finish before Traefik stops.
Can be provided in a format supported by [time.ParseDuration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#ParseDuration) or as raw values (digits).
If no units are provided, the value is parsed assuming seconds.
!!! warning "In this time frame no new requests are accepted."
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.name]
address = ":8888"
[entryPoints.name.transport]
[entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle]
graceTimeOut = 42
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
name:
address: ":8888"
transport:
lifeCycle:
graceTimeOut: 42
```
```bash tab="CLI"
## Static configuration
--entryPoints.name.address=:8888
--entryPoints.name.transport.lifeCycle.graceTimeOut=42
```
ProxyProtocol
Traefik supports ProxyProtocol version 1 and 2.
If Proxy Protocol header parsing is enabled for the entry point, this entry point can accept connections with or without Proxy Protocol headers.
If the Proxy Protocol header is passed, then the version is determined automatically.
??? info "proxyProtocol.trustedIPs"
Enabling Proxy Protocol with Trusted IPs.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.web.proxyProtocol]
trustedIPs = ["127.0.0.1/32", "192.168.1.7"]
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
proxyProtocol:
trustedIPs:
- "127.0.0.1/32"
- "192.168.1.7"
```
```bash tab="CLI"
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
--entryPoints.web.proxyProtocol.trustedIPs=127.0.0.1/32,192.168.1.7
```
IPs in `trustedIPs` only will lead to remote client address replacement: Declare load-balancer IPs or CIDR range here.
??? info "proxyProtocol.insecure"
Insecure Mode (Testing Environment Only).
In a test environments, you can configure Traefik to trust every incoming connection.
Doing so, every remote client address will be replaced (`trustedIPs` won't have any effect)
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
## Static configuration
[entryPoints]
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.web.proxyProtocol]
insecure = true
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
## Static configuration
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
proxyProtocol:
insecure: true
```
```bash tab="CLI"
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
--entryPoints.web.proxyProtocol.insecure
```
!!! warning "Queuing Traefik behind Another Load Balancer"
When queuing Traefik behind another load-balancer, make sure to configure Proxy Protocol on both sides.
Not doing so could introduce a security risk in your system (enabling request forgery).
HTTP Options
This whole section is dedicated to options, keyed by entry point, that will apply only to HTTP routing.
Redirection
??? example "HTTPS redirection (80 to 443)"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
[entryPoints.web]
address = ":80"
[entryPoints.web.http]
[entryPoints.web.http.redirections]
[entryPoints.web.http.redirections.entryPoint]
to = "websecure"
scheme = "https"
[entryPoints.websecure]
address = ":443"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
entryPoints:
web:
address: :80
http:
redirections:
entryPoint:
to: websecure
scheme: https
websecure:
address: :443
```
```bash tab="CLI"
--entrypoints.web.address=:80
--entrypoints.web.http.redirections.entryPoint.to=websecure
--entrypoints.web.http.redirections.entryPoint.https=true
--entrypoints.websecure.address=:443
```
entryPoint
This section is a convenience to enable (permanent) redirecting of all incoming requests on an entry point (e.g. port 80) to another entry point (e.g. port 443).
??? info "entryPoint.to"
_Required_
The target entry point.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
[entryPoints.foo]
# ...
[entryPoints.foo.http.redirections]
[entryPoints.foo.http.redirections.entryPoint]
to = "bar"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
entryPoints:
foo:
# ...
http:
redirections:
entryPoint:
to: bar
```
```bash tab="CLI"
--entrypoints.foo.http.redirections.entryPoint.to=websecure
```
??? info "entryPoint.scheme"
_Optional, Default="http"_
The redirection target scheme.
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
[entryPoints.foo]
# ...
[entryPoints.foo.http.redirections]
[entryPoints.foo.http.redirections.entryPoint]
# ...
scheme = "https"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
entryPoints:
foo:
# ...
http:
redirections:
entryPoint:
# ...
scheme: https
```
```bash tab="CLI"
--entrypoints.foo.http.redirections.entryPoint.scheme=https
```
Middlewares
The list of middlewares that are prepended by default to the list of middlewares of each router associated to the named entry point.
[entryPoints.websecure]
address = ":443"
[entryPoints.websecure.http]
middlewares = ["auth@file", "strip@file"]
entryPoints:
websecure:
address: ':443'
http:
middlewares:
- auth@file
- strip@file
entrypoints.websecure.address=:443
entrypoints.websecure.http.middlewares=auth@file,strip@file
TLS
This section is about the default TLS configuration applied to all routers associated with the named entry point.
If a TLS section (i.e. any of its fields) is user-defined, then the default configuration does not apply at all.
The TLS section is the same as the TLS section on HTTP routers.
[entryPoints.websecure]
address = ":443"
[entryPoints.websecure.http.tls]
options = "foobar"
certResolver = "leresolver"
[[entryPoints.websecure.http.tls.domains]]
main = "example.com"
sans = ["foo.example.com", "bar.example.com"]
[[entryPoints.websecure.http.tls.domains]]
main = "test.com"
sans = ["foo.test.com", "bar.test.com"]
entryPoints:
websecure:
address: ':443'
http:
tls:
options: foobar
certResolver: leresolver
domains:
- main: example.com
sans:
- foo.example.com
- bar.example.com
- main: test.com
sans:
- foo.test.com
- bar.test.com
entrypoints.websecure.address=:443
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.options=foobar
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.certResolver=leresolver
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.domains[0].main=example.com
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.domains[0].sans=foo.example.com,bar.example.com
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.domains[1].main=test.com
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.domains[1].sans=foo.test.com,bar.test.com
??? example "Let's Encrypt"
```toml tab="File (TOML)"
[entryPoints.websecure]
address = ":443"
[entryPoints.websecure.http.tls]
certResolver = "leresolver"
```
```yaml tab="File (YAML)"
entryPoints:
websecure:
address: ':443'
http:
tls:
certResolver: leresolver
```
```bash tab="CLI"
entrypoints.websecure.address=:443
entrypoints.websecure.http.tls.certResolver=leresolver
```