# Importing a model
## Table of Contents
* [Importing a Safetensors adapter](#Importing-a-fine-tuned-adapter-from-Safetensors-weights)
* [Importing a Safetensors model](#Importing-a-model-from-Safetensors-weights)
* [Importing a GGUF file](#Importing-a-GGUF-based-model-or-adapter)
* [Sharing models on ollama.com](#Sharing-your-model-on-ollamacom)
## Importing a fine tuned adapter from Safetensors weights
First, create a `Modelfile` with a `FROM` command pointing at the base model you used for fine tuning, and an `ADAPTER` command which points to the directory with your Safetensors adapter:
```dockerfile
FROM
ADAPTER /path/to/safetensors/adapter/directory
```
Make sure that you use the same base model in the `FROM` command as you used to create the adapter otherwise you will get erratic results. Most frameworks use different quantization methods, so it's best to use non-quantized (i.e. non-QLoRA) adapters. If your adapter is in the same directory as your `Modelfile`, use `ADAPTER .` to specify the adapter path.
Now run `ollama create` from the directory where the `Modelfile` was created:
```bash
ollama create my-model
```
Lastly, test the model:
```bash
ollama run my-model
```
Ollama supports importing adapters based on several different model architectures including:
* Llama (including Llama 2, Llama 3, and Llama 3.1);
* Mistral (including Mistral 1, Mistral 2, and Mixtral); and
* Gemma (including Gemma 1 and Gemma 2)
You can create the adapter using a fine tuning framework or tool which can output adapters in the Safetensors format, such as:
* Hugging Face [fine tuning framework] (https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/training)
* [Unsloth](https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth)
* [MLX](https://github.com/ml-explore/mlx)
## Importing a model from Safetensors weights
First, create a `Modelfile` with a `FROM` command which points to the directory containing your Safetensors weights:
```dockerfile
FROM /path/to/safetensors/directory
```
If you create the Modelfile in the same directory as the weights, you can use the command `FROM .`.
Now run the `ollama create` command from the directory where you created the `Modelfile`:
```shell
ollama create my-model
```
Lastly, test the model:
```shell
ollama run my-model
```
Ollama supports importing models for several different architectures including:
* Llama (including Llama 2, Llama 3, and Llama 3.1);
* Mistral (including Mistral 1, Mistral 2, and Mixtral);
* Gemma (including Gemma 1 and Gemma 2); and
* Phi3
This includes importing foundation models as well as any fine tuned models which which have been _fused_ with a foundation model.
## Importing a GGUF based model or adapter
If you have a GGUF based model or adapter it is possible to import it into Ollama. You can obtain a GGUF model or adapter by:
* converting a Safetensors model with the `convert_hf_to_gguf.py` from Llama.cpp;
* converting a Safetensors adapter with the `convert_lora_to_gguf.py` from Llama.cpp; or
* downloading a model or adapter from a place such as HuggingFace
To import a GGUF model, create a `Modelfile` containg:
```dockerfile
FROM /path/to/file.gguf
```
For a GGUF adapter, create the `Modelfile` with:
```dockerfile
FROM
ADAPTER /path/to/file.gguf
```
When importing a GGUF adapter, it's important to use the same base model as the base model that the adapter was created with. You can use:
* a model from Ollama
* a GGUF file
* a Safetensors based model
Once you have created your `Modelfile`, use the `ollama create` command to build the model.
```shell
ollama create my-model
```
## Quantizing a Model
Quantizing a model allows you to run models faster and with less memory consumption but at reduced accuracy. This allows you to run a model on more modest hardware.
Ollama can quantize FP16 and FP32 based models into different quantization levels using the `-q/--quantize` flag with the `ollama create` command.
First, create a Modelfile with the FP16 or FP32 based model you wish to quantize.
```dockerfile
FROM /path/to/my/gemma/f16/model
```
Use `ollama create` to then create the quantized model.
```shell
$ ollama create --quantize q4_K_M mymodel
transferring model data
quantizing F16 model to Q4_K_M
creating new layer sha256:735e246cc1abfd06e9cdcf95504d6789a6cd1ad7577108a70d9902fef503c1bd
creating new layer sha256:0853f0ad24e5865173bbf9ffcc7b0f5d56b66fd690ab1009867e45e7d2c4db0f
writing manifest
success
```
### Supported Quantizations
- `q4_0`
- `q4_1`
- `q5_0`
- `q5_1`
- `q8_0`
#### K-means Quantizations
- `q3_K_S`
- `q3_K_M`
- `q3_K_L`
- `q4_K_S`
- `q4_K_M`
- `q5_K_S`
- `q5_K_M`
- `q6_K`
## Sharing your model on ollama.com
You can share any model you have created by pushing it to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com) so that other users can try it out.
First, use your browser to go to the [Ollama Sign-Up](https://ollama.com/signup) page. If you already have an account, you can skip this step.
 The `Username` field will be used as part of your model's name (e.g. `jmorganca/mymodel`), so make sure you are comfortable with the username that you have selected.
Now that you have created an account and are signed-in, go to the [Ollama Keys Settings](https://ollama.com/settings/keys) page.
Follow the directions on the page to determine where your Ollama Public Key is located.
The `Username` field will be used as part of your model's name (e.g. `jmorganca/mymodel`), so make sure you are comfortable with the username that you have selected.
Now that you have created an account and are signed-in, go to the [Ollama Keys Settings](https://ollama.com/settings/keys) page.
Follow the directions on the page to determine where your Ollama Public Key is located.
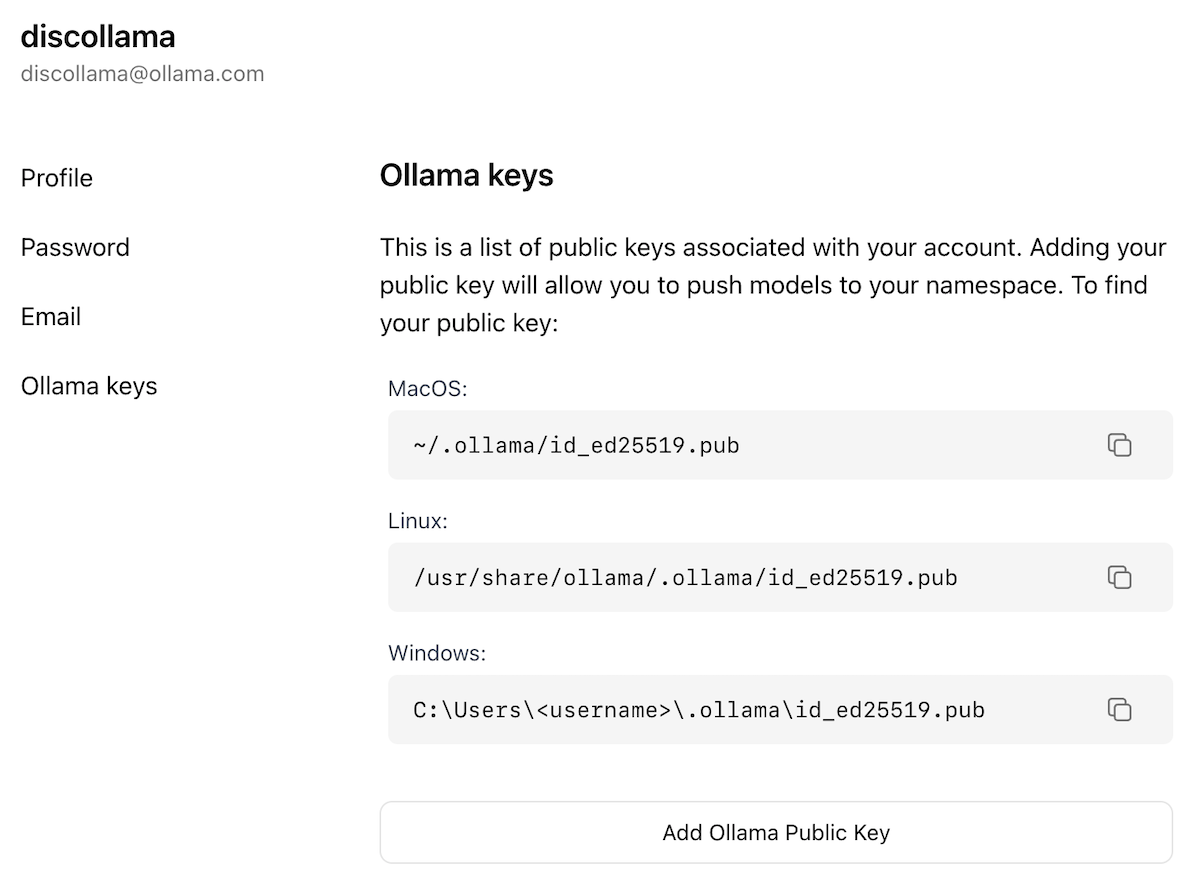 Click on the `Add Ollama Public Key` button, and copy and paste the contents of your Ollama Public Key into the text field.
To push a model to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com), first make sure that it is named correctly with your username. You may have to use the `ollama cp` command to copy
your model to give it the correct name. Once you're happy with your model's name, use the `ollama push` command to push it to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com).
```shell
ollama cp mymodel myuser/mymodel
ollama push myuser/mymodel
```
Once your model has been pushed, other users can pull and run it by using the command:
```shell
ollama run myuser/mymodel
```
Click on the `Add Ollama Public Key` button, and copy and paste the contents of your Ollama Public Key into the text field.
To push a model to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com), first make sure that it is named correctly with your username. You may have to use the `ollama cp` command to copy
your model to give it the correct name. Once you're happy with your model's name, use the `ollama push` command to push it to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com).
```shell
ollama cp mymodel myuser/mymodel
ollama push myuser/mymodel
```
Once your model has been pushed, other users can pull and run it by using the command:
```shell
ollama run myuser/mymodel
```
 The `Username` field will be used as part of your model's name (e.g. `jmorganca/mymodel`), so make sure you are comfortable with the username that you have selected.
Now that you have created an account and are signed-in, go to the [Ollama Keys Settings](https://ollama.com/settings/keys) page.
Follow the directions on the page to determine where your Ollama Public Key is located.
The `Username` field will be used as part of your model's name (e.g. `jmorganca/mymodel`), so make sure you are comfortable with the username that you have selected.
Now that you have created an account and are signed-in, go to the [Ollama Keys Settings](https://ollama.com/settings/keys) page.
Follow the directions on the page to determine where your Ollama Public Key is located.
 Click on the `Add Ollama Public Key` button, and copy and paste the contents of your Ollama Public Key into the text field.
To push a model to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com), first make sure that it is named correctly with your username. You may have to use the `ollama cp` command to copy
your model to give it the correct name. Once you're happy with your model's name, use the `ollama push` command to push it to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com).
```shell
ollama cp mymodel myuser/mymodel
ollama push myuser/mymodel
```
Once your model has been pushed, other users can pull and run it by using the command:
```shell
ollama run myuser/mymodel
```
Click on the `Add Ollama Public Key` button, and copy and paste the contents of your Ollama Public Key into the text field.
To push a model to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com), first make sure that it is named correctly with your username. You may have to use the `ollama cp` command to copy
your model to give it the correct name. Once you're happy with your model's name, use the `ollama push` command to push it to [ollama.com](https://ollama.com).
```shell
ollama cp mymodel myuser/mymodel
ollama push myuser/mymodel
```
Once your model has been pushed, other users can pull and run it by using the command:
```shell
ollama run myuser/mymodel
```